Estimated reading time: 12 minutes

Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Unfortunately, much like curly hair on a humid day, SEO is not set-it-and-forget-it. It takes constant work and upkeep. We’ve provided tips, tricks and checklists in the past for optimizing your on-page SEO, but there’s always room for improvement. And within your optimization efforts, things may swing too far in the wrong direction. In addition to our Checklist for DIY Organic Growth through On-Page SEO, we also want to provide you with this guide on some of the most common on-page SEO errors, and how to fix them.
What Is On-Page SEO?
Again, this isn’t our first time talking about this topic, so if you’re a regular reader of our blog, you may already be familiar with the term. Feel free to let your mind wander, as we explain for the new visitors.
There are a few different types of search engine optimization (SEO) branches. For instance, technical SEO has to do with the coding of your site. Unless you’ve taken up SEO and website code in your spare time, you’re likely going to need an expert to help you with this.
On-page SEO is generally more accessible for the average store owner. While it can get complicated, depending on your level of experience and dedication, you can absolutely manage these things yourself. They are the SEO strategies that take place directly on the pages of your website that dictate how users and search engine crawlers perceive your site.
How Do On-Page SEO Errors Happen?
Despite your best efforts, you are probably going to run into SEO errors. With so many gears turning at once, it can be a full time job to keep up with the constant changes and adjustments that may need to be made to a site over time. But why do some aspects of your SEO turn into errors all of a sudden?
Browser and Device Updates
As internment browsers and device operating systems update, they begin processing information differently. That may cause disruption in the way your modules or code runs, or how quickly your site loads, for example.
Search Engine Updates
An example of this is the core update coming to Google in May which focuses largely on page load speed and layout. As search engines develop and respond to market demands, they begin wanting new specifications to be met by the sites that they show in search results.
Changing User Expectations
User expectations change over time, which often play into the shift in search engine requirements. Shoppers want increasingly faster, more optimized and personalized content, and search engines want to deliver that.
But when user expectations change, your site will be the first thing that experiences the effects, not the search engines. A drop in clicks, a rise in bounce rate, and an increase in cart abandonment are all tell-tale signs that something is suddenly no longer making the cut for your shoppers.
Content Changes
Depending on how you run your store, and the products and content you offer, you may be making relatively frequent updates. While your original copy may have been expertly and carefully crafted to suit SEO specifications, subsequent additions or edits may have detracted from the effectiveness.
Third-Party Site Changes
Do you link to third-party sites anywhere on your pages? Perhaps it’s a manufacturer details page, a downloadable information sheet from a supplier, or an interesting blog post from someone else in the industry. Maybe you have YouTube videos or social media posts embedded in your blogs? If the owner of those third-party assets changes, removes, or disables them in any way, you may be looking at broken links, videos or images without even realizing it.
Common On-Page SEO Errors & How To Fix Them
1. Site Speed
Site speed – specifically page load speed – has always been important but has a new spotlight shone on it thanks to Google’s new update focusing on Core Web Vitals. Despite the internet being comprised of technical mumbo-jumbo, page speed isn’t really an exact science.
There are plenty of page and speed tools available for free on the internet. We have a guide to checking and managing your site speed that walks you through using a few of them. But in reality, because there are so many factors that can play into the loading time, you can’t take any of the speed measurement tools as an exact calculation.
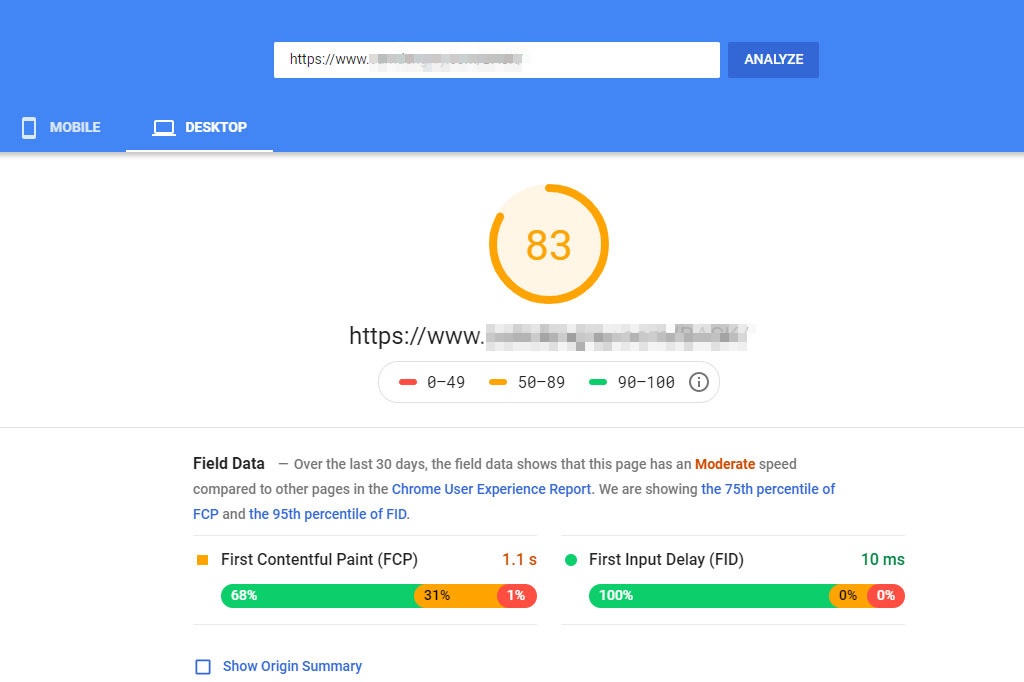
Follow the guide we have to try and pinpoint any serious issues with your page speed, but don’t obsess over the numbers in the tools. Here are a few things you can do to speed up your loading time:
- Optimize your images for web. Too many large images on a page will slow things down.
- Embed your videos. Upload them to a third-party site like YouTube then link them in via URL; don’t host them on your site.
- Reconsider animations. If you have animated graphics on your site, make sure they are really worth the impact. They can really add to your load time.
- Consider Lazy Loading. If you need to have a lot of images, our Lazy Load feature helps to prioritize the loading to optimize page speed.
2. Incorrect Linking
Having both internal and outbound links on your site can help and hurt your SEO, depending on how it’s done. We already touched on broken links when discussing third-party site changes, but that’s just one way you can go wrong with your on-page linking.
Too many links, for example, can cause SEO errors for you. Aside from looking spammy, and leaving you vulnerable to plenty of broken links, it can also cause issues with usability.
With too many links in a single page, it can raise flags for search engines, particularly when it comes to the mobile experience. If your paragraph of text is full of in-line links, they become too difficult for the user to tap. You’ll likely end up with the error “Clickable elements too close together”. Only add them if they actually add value to your user.
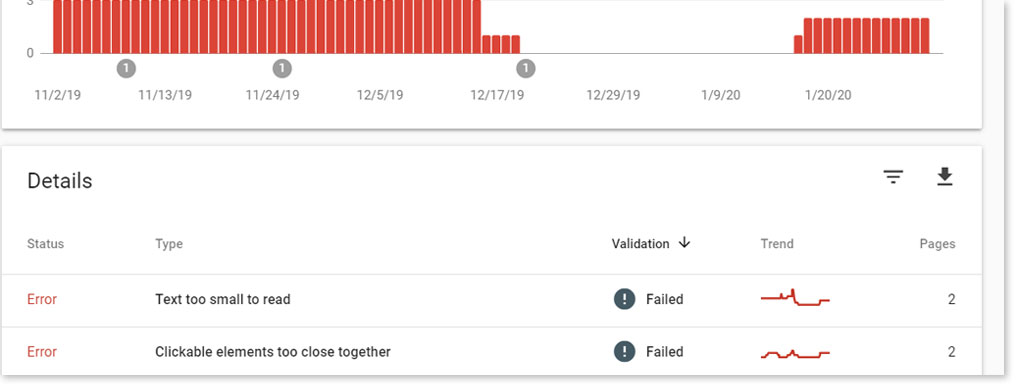
In the same vein of being selective with your links, you should also be careful about where the links take your users. Redirecting users to a low-quality site can negatively affect your own site authority. In short, have links, but focus on quality over quantity.
- Find and fix broken links. Use a tool like Google’s Chrome extension Check My Links to suss out the broken links. If the content has been moved or renamed, replace the link. If the link destination no longer exists, find something else to replace it, or remove the link all together. This applies to your images as well, which will have the same result if broken or missing.
- Get rid of unnecessary links. If the content doesn’t need a link, remove it. If it’s critical to have those links provided on your page, talk to your developer to come up with an alternate way to display them.
- Trust the link destinations. In a way, links make you guilty by association. Provide links to high-quality, high-authority sites to help boost your user experience and your ranking.
3. Duplicate Content
Particularly for eCommerce sites, duplicate content may seem completely unavoidable. If you sell 20 different t-shirts, how many different ways can you really say that it’s 100% cotton, available in a range of sizes, and is machine washable? Google does understand this and so handles duplicate content differently from other on-page SEO errors:
“Duplicate content on a site is not grounds for action on that site unless it appears that the intent of the duplicate content is to be deceptive and manipulate search engine results.”
You usually won’t get a negative score from the search engines if they find duplicate content on your site. Instead, they simply don’t give you credit for those pages; the search engine will decide which page to show as the originator of the content and disregard the rest. So while you aren’t actively getting dinged with a penalty, you may be at risk for the wrong page getting the SEO hits. You’re also losing out on other potential ranking opportunities within those skipped pages.
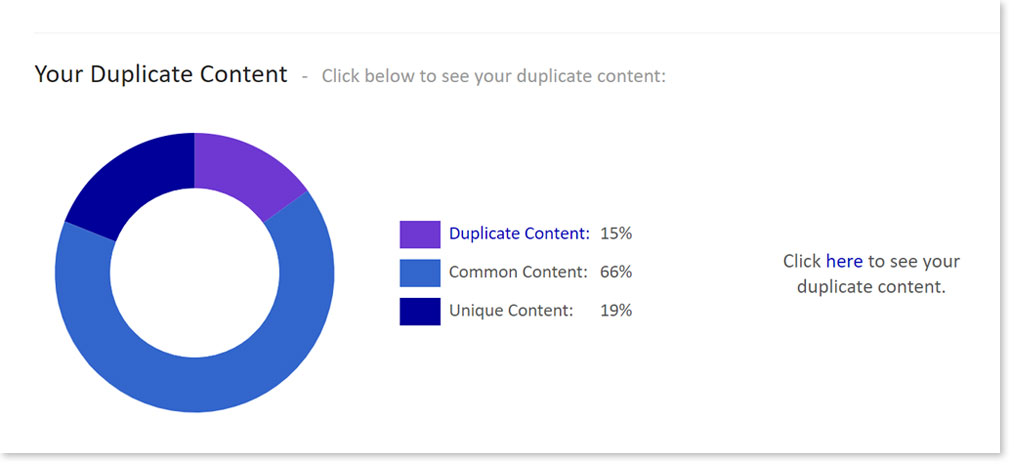
- Add unique content. You can’t get away from having a list of specifications that may be identical to other sites on the web. Counteract that duplication by providing unique content. Before providing the list of specs, speak about the product from your own unique perspective to create a rich product description.
- Check for duplicate content regularly. There are free tools at your disposal to track down duplicate content on your site.
- Contact your developer. If you’ve done what you can to avoid duplicate content, but the tools above still report some issues, there are pieces of code that can help dictate which of your site pages should be considered primary by the search engines. Reach out to your developer to help implement those.
4. Missing Image Alt Tags
Alt (alternative) text tags are pieces of text that you apply to your images to describe what is being shown. They are used in a couple of ways. For one, they help with accessibility so visually impaired visitors can experience and understand the image content on your site. Search engines are constantly trying to improve the user experience, and that includes accessibility. In addition, search engines use this information to properly index your images and ensure they show up in image search results.
It’s for both of those reasons that missing your alt text can result in on-page SEO errors, and lowered ranking.
- In Miva: When adding images to your site for things like logos, banners, and promotional sections, you have the option to add in your Alt Text. For product images, the product page templates, by default, use your product name to provide the text.
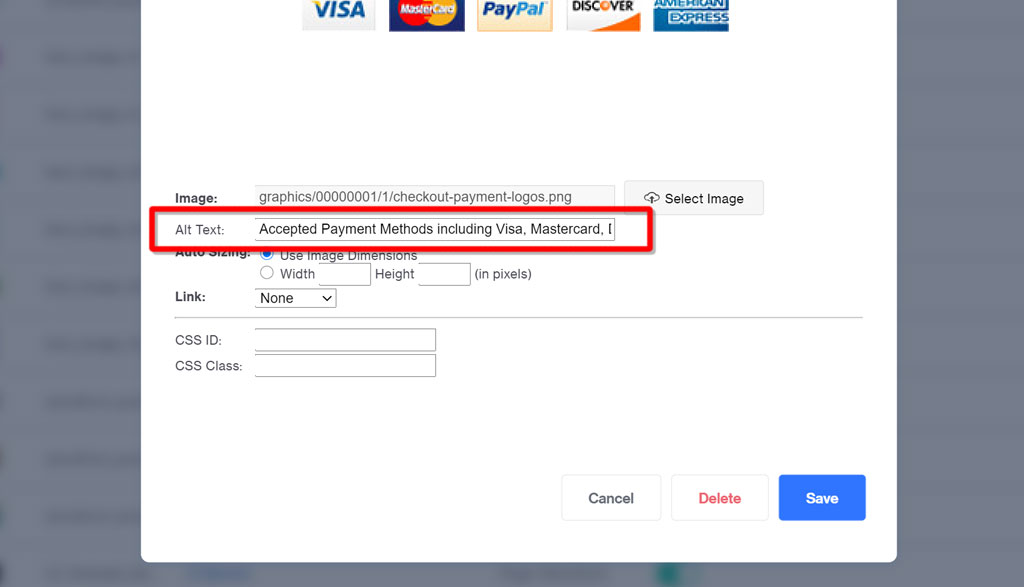
- Outside of Miva: If you use something other than Miva for your store, blog, or informational website, you may need to add the Alt Text via a simple string of HTML code: <img src=“image.jpg” alt=“image description”>. For example:
| <img src=“checkout-payment-logos.png” alt=“Accepted Payment Methods including Visa, Mastercard, Discover, Amex”> |
5. Low Word Count
This one can be tricky to navigate. While search engines don’t specify a minimum word count, they may consider your low-word-count pages to be “thin” or “low value”, referring to the value you can offer your readers. Giving preference to higher-value pages means your “low value” content may be bypassed when offering results to searchers.
Aside from not ranking well, low word count can present as an on-page SEO error because it’s less likely you’ll be able to get in enough keywords in a meaningful way. From there, you’ll either have to resort to keyword stuffing or simply not ranking for the page.
- Increase word count. Where possible, aim for higher word counts, in the 1500-2000 range. If you can successfully write content longer than that, even better.
- Aim for long-tail keywords. It will be harder to rank your content for short keywords (ie. Lemon Balm) than longer, more descriptive keywords known as “long-tail” (ie. Loose Leaf Lemon Balm Tea).
6. Problems in Title & H1 Tags
Title and H1 tags are the text on your pages used to create a hierarchy. They let the search engines know what information is important, and what to display on the search result page.
There are a range of issues that can arise between the two tag types that result in on-page SEO errors. So many, in fact, that it might be a little frustrating bouncing between them all to make sure you strike the right balance. However, they are the first things your user sees on the search result page, and are generally the first thing they see if they click through. They need to have the right impact in order to encourage the user to keep reading, ultimately boosting your analytics and subsequently, your ranking.
- Missing tags. While title and H1 tags seem similar, they aren’t the same! Your pages need both, and missing either one can hurt your SEO.
- Duplicate tags. If you use the same title tag for multiple pages on your site, they become essentially useless and search engines will find other content to use for your page title. This may be to your detriment. However, you can duplicate your title tag in your H1 tag! Yes, you can use the same copy for both your title and H1 tags on the same piece of content.
- Include your keyword. The title and H1 tags show your users and the search engines what your content is about, so make sure you include your keywords!
- Not too long, not too short. Take advantage of the space you’re given for your title and H1 tags, but use it wisely. You need to be able to include your keywords, display what makes your content special or exciting, and provide a solution as to why users should select your result. But keep in mind that search engines will truncate (cut off) your title if they have too many characters. Aim for the 50-60 character range.
An online tool like Screaming Frog is often recommended to check your site for issues with your title and H1 tags. Run your site through the tool and if you need help addressing missing or incorrect tags, contact your developer.
Working Through Your On-Page SEO Errors
Unfortunately, SEO is a long-game, and it’s a necessary one. It seems like nothing is more frustrating than working endlessly to improve something that shows no immediate results. But don’t give up on your efforts.
Making the changes and corrections above will get easier in time, and pretty soon, implementing them into your daily workflows will be second nature. But in the meantime, stay vigilant and don’t get discouraged when the search engines change their ranking requirements. Above all, focus on creating valuable, user-first content and the rest should fall into place. For anything you can’t manage on your own, we can help. If you run into any issues in correcting your on-page SEO errors, contact us.